IA, Data, Annotation & Innovation, découvrez le blog d’Infoscribe.ai
La synergie entre expertise humaine et technologies avancées au service de la donnée.
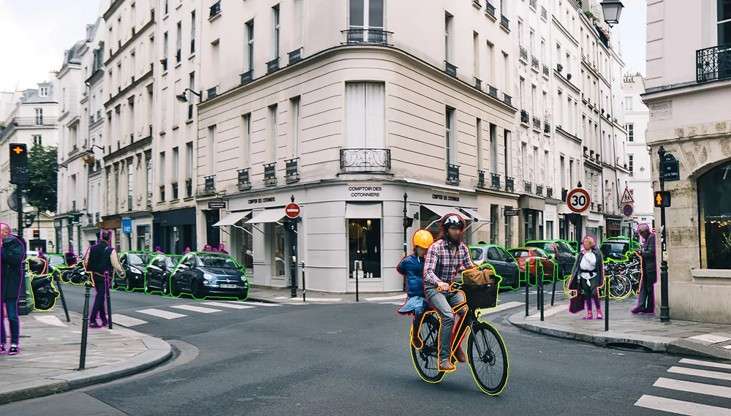

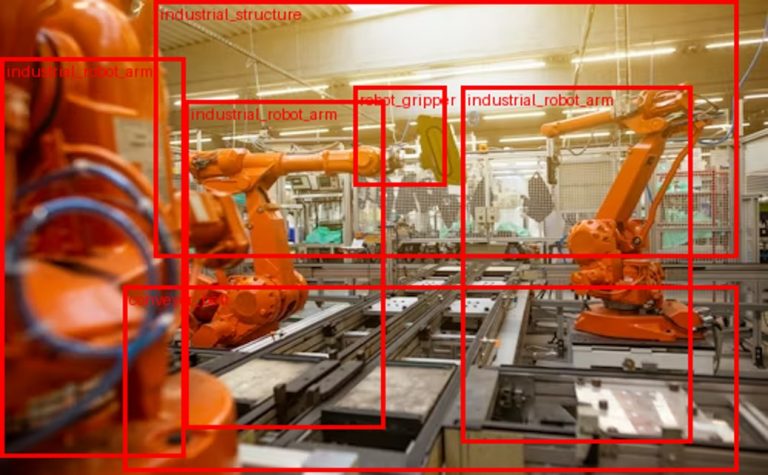
La computer vision est devenue l’un des piliers de l’intelligence artificielle moderne. Grâce aux avancées...
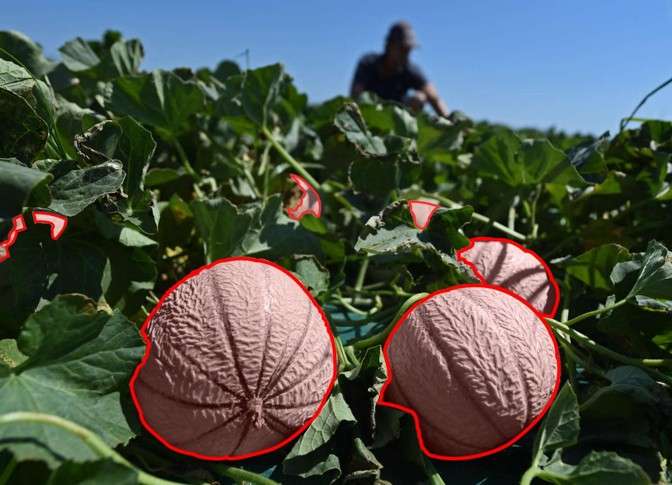

L’intelligence artificielle s’impose aujourd’hui comme l’un des leviers les plus puissants pour faire...
No posts found