The field of computer vision has witnessed remarkable advancements in recent decades. In this article, we will explore the period from 2000 to the present, highlighting significant milestones, key players, and breakthroughs that have shaped the evolution of computer vision during this time.
Rise of Deep Learning and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs):
In the early 2000s, deep learning emerged as a powerful approach in computer vision. Researchers such as Yann LeCun, Geoffrey Hinton, and Yoshua Bengio pioneered the development of deep neural networks, particularly CNNs, which revolutionized object recognition, image classification, and image segmentation tasks. The breakthroughs in deep learning laid the foundation for many subsequent advancements in computer vision.
ImageNet Challenge and the Birth of Large-Scale Visual Recognition:
In 2009, the ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge (ILSVRC) was introduced, spurring significant progress in object detection and classification. Teams led by Fei-Fei Li and Alex Krizhevsky achieved groundbreaking results using deep CNNs, demonstrating the potential of large-scale visual recognition and the importance of curated datasets for training and evaluation.
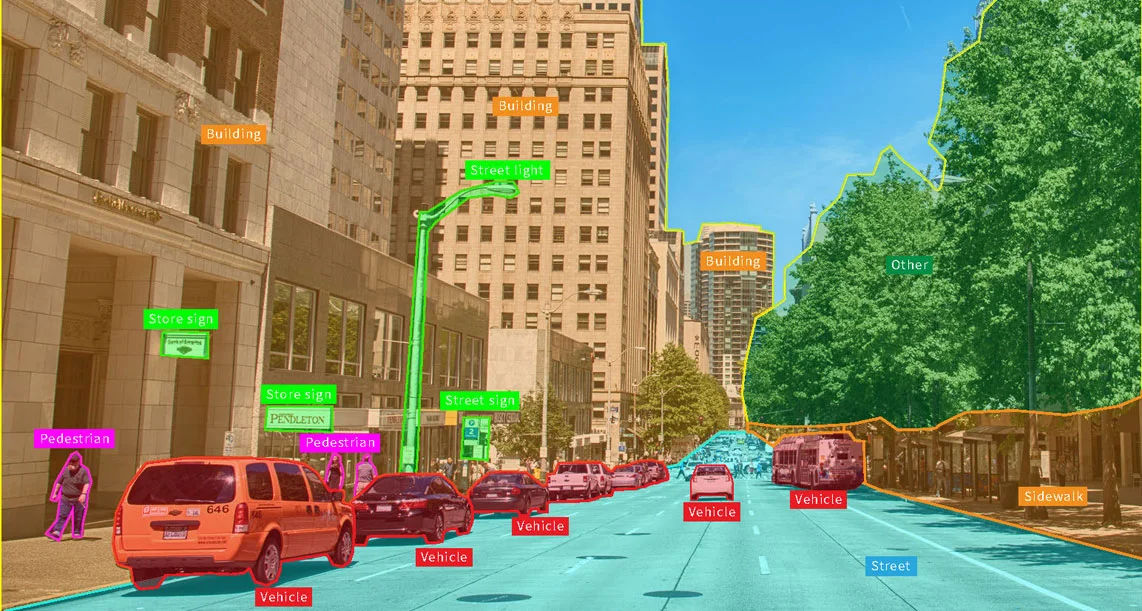
Autonomous Vehicles and Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS):
The 2010s saw rapid advancements in computer vision for autonomous vehicles and ADAS. Companies like Waymo, Tesla, and Mobileye developed sophisticated computer vision systems that enable vehicles to perceive their surroundings, detect objects, and make intelligent driving decisions. Techniques such as object detection, lane detection, and pedestrian recognition have contributed to enhancing road safety and driving automation.
Face Recognition and Biometrics:
Face recognition technology has made significant strides in recent years. Notable contributions have come from researchers such as Li Fei-Fei, Gary Bradski, and Yaniv Taigman. Face recognition algorithms, combined with advancements in deep learning, have enabled applications in identity verification, access control, and surveillance systems.
Augmented Reality and Mixed Reality:
Computer vision plays a crucial role in enabling augmented reality (AR) and mixed reality (MR) experiences. Companies like Apple, Google, and Microsoft have developed AR platforms and devices, such as Apple ARKit, Google ARCore, and Microsoft HoloLens, which rely on computer vision algorithms to track and overlay digital content onto the real world in real-time.
Medical Imaging and Healthcare:
Computer vision has found significant applications in medical imaging and healthcare. Researchers and companies, including Google Health and IBM Watson Health, have developed algorithms for automated diagnosis, medical image analysis, and disease detection. Computer vision techniques, such as tumor segmentation, lesion detection, and image-based pathology, have the potential to improve patient care and assist healthcare professionals in making accurate diagnoses.
From the advancements in deep learning and CNNs to the applications in autonomous vehicles, face recognition, augmented reality, and medical imaging, computer vision has witnessed tremendous progress since 2000. The contributions of pioneers such as LeCun, Hinton, and Li, along with the efforts of research institutions and industry leaders, have shaped the field and opened doors to exciting possibilities. As computer vision continues to evolve, we can expect further breakthroughs that will reshape industries, improve everyday lives, and push the boundaries of what is possible.
 APPOINTMENT
APPOINTMENT