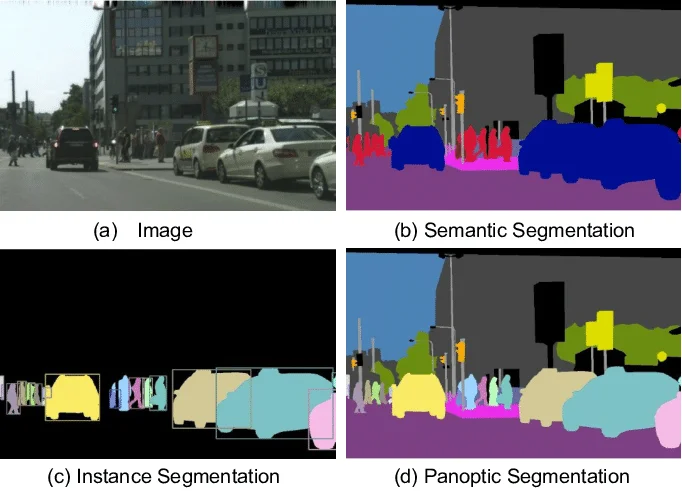
In the field of computer vision, image segmentation plays a crucial role in extracting meaningful information from visual data. There are three main types of image segmentation techniques: instance segmentation, semantic segmentation, and panoptic segmentation. In this article, we will explore the differences between these methods and their applications in various industries.
Semantic Segmentation:
Semantic segmentation focuses on classifying each pixel into specific object categories or regions, providing a detailed understanding of the different components in an image. It is commonly used in medical imaging for organ segmentation, scene understanding, and image segmentation tasks. Semantic segmentation is crucial for tasks that require a holistic view of the scene and is widely used in the healthcare and autonomous driving industries.
Instance Segmentation:
Instance segmentation is a pixel-level annotation technique that goes beyond semantic segmentation. It not only classifies each pixel into different object categories but also distinguishes individual instances of the same category within the image. For example, in a scene with multiple cars, instance segmentation would label each car separately, allowing for precise localization and tracking. This type of segmentation is particularly useful in robotics, object tracking, and autonomous vehicles.
Panoptic Segmentation:
Panoptic segmentation is a combination of instance and semantic segmentation, aiming to provide a comprehensive analysis of the entire scene. It not only labels individual instances but also assigns a category label to background regions. In other words, panoptic segmentation unifies object instances and stuff (background elements) into a single result. This technique is particularly valuable in understanding complex visual scenes and is applied in robotics, urban planning, and environmental monitoring.
Key Differences:
The main difference between these segmentation techniques lies in the level of detail they offer. Instance segmentation provides precise information about each individual object, while semantic segmentation focuses on classifying entire regions. Panoptic segmentation combines both approaches, offering a unified view of the scene.
Applications:
Instance segmentation finds applications in various fields, such as object detection, pose estimation, and human-computer interaction. Semantic segmentation is widely used in medical imaging, scene understanding, and autonomous vehicles. Panoptic segmentation is valuable in urban planning, environmental monitoring, and robotics.
Image segmentation techniques - instance segmentation, semantic segmentation, and panoptic segmentation - each serve specific purposes in computer vision applications. Understanding their differences and applications is crucial for leveraging the full potential of visual data in diverse industries.
Discover the power of image segmentation with InfoScribe's comprehensive annotation services:
https://infoscribe.ai/en/
 APPOINTMENT
APPOINTMENT