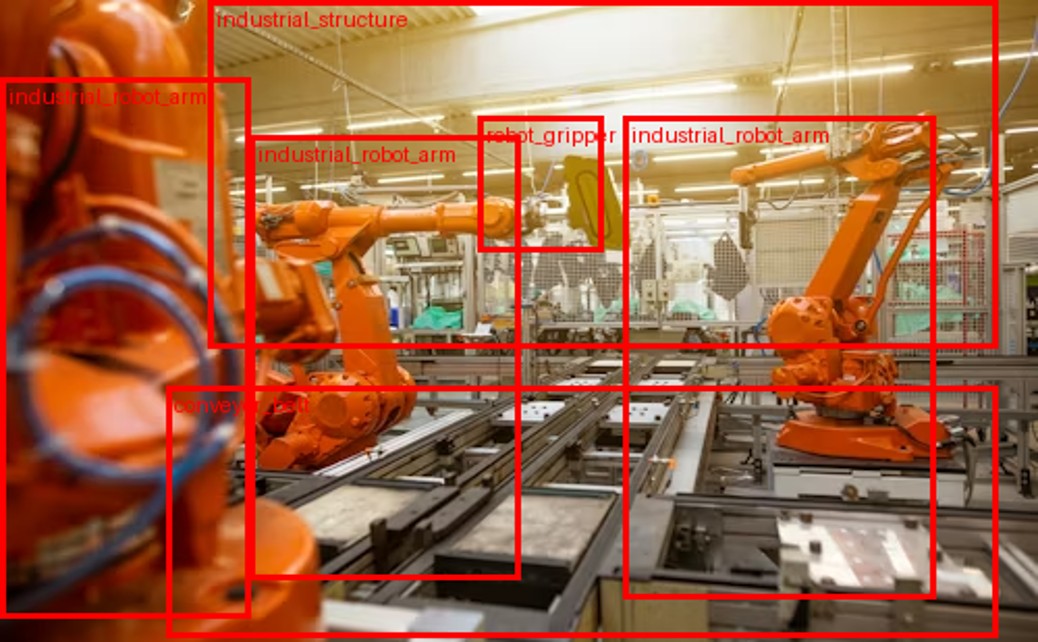
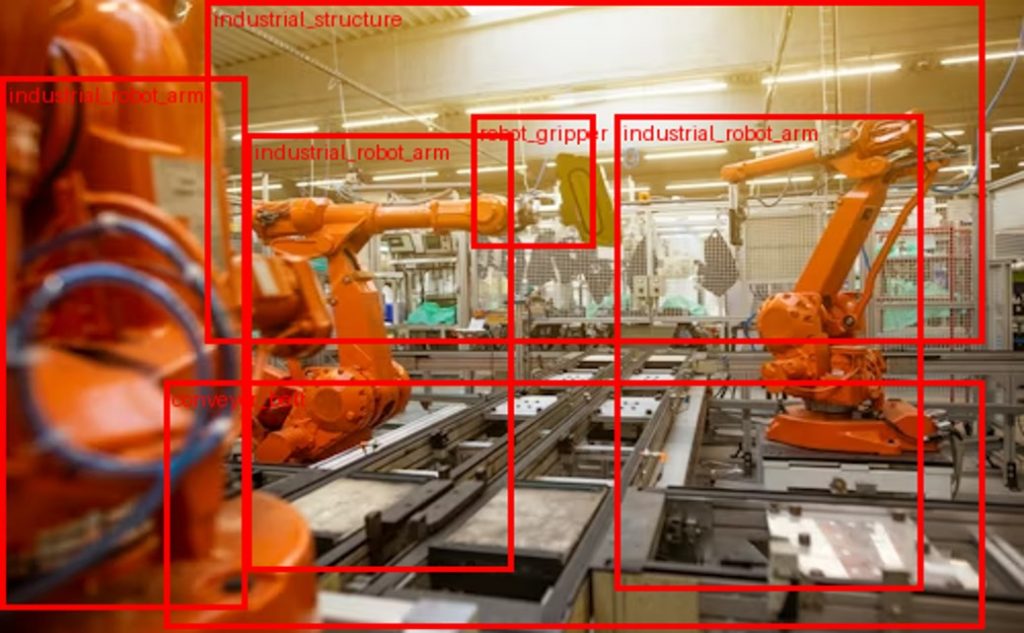
Why Data Annotation Is Becoming a Strategic Priority for Industry
The global industry is undergoing a profound transformation driven by artificial intelligence, automation, and the increasing importance of data. In this context, computer vision is emerging as one of the most foundational technological pillars for the years ahead. Whether it is for automated quality control, predictive maintenance, operator safety, or logistics optimization, the ability of machines to interpret images, videos, and sensor streams is radically transforming industrial processes. Yet, behind the impressive performance of algorithms, one element is still too often underestimated: data annotation.
The future of industrial AI depends not only on the power of deep learning models but, above all, on the quality of the data on which these models are trained. As industrial environments become more complex, more automated, and more interconnected, the question of 2D and 3D annotation becomes central.
Industrial Computer Vision Facing Increasingly Complex Environments
In industrial settings, computer vision is not limited to recognizing simple objects under ideal conditions. It must operate in constrained, sometimes hazardous, and highly variable contexts, where even a small mistake can result in significant financial losses or jeopardize human safety. Industrial images are rarely perfect and present specific challenges related to lighting, camera angles, and the diversity of scenarios.
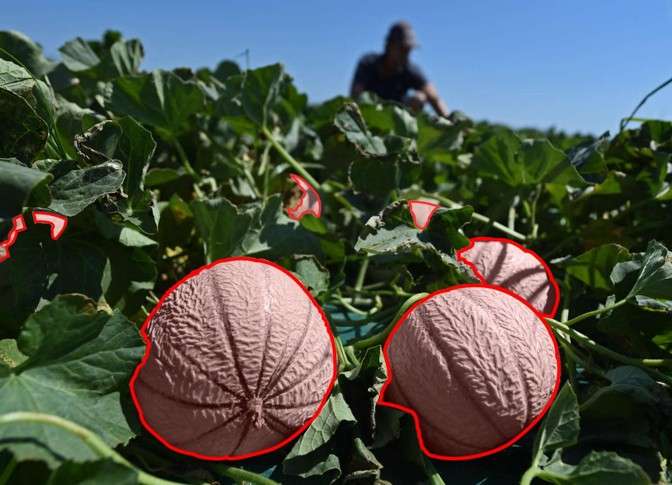
In this context, 2D and 3D annotation plays a fundamental role in translating physical reality into data that algorithms can exploit. Segmentation provides the level of precision required to detect critical—sometimes subtle—defects that would be invisible to simpler methods.
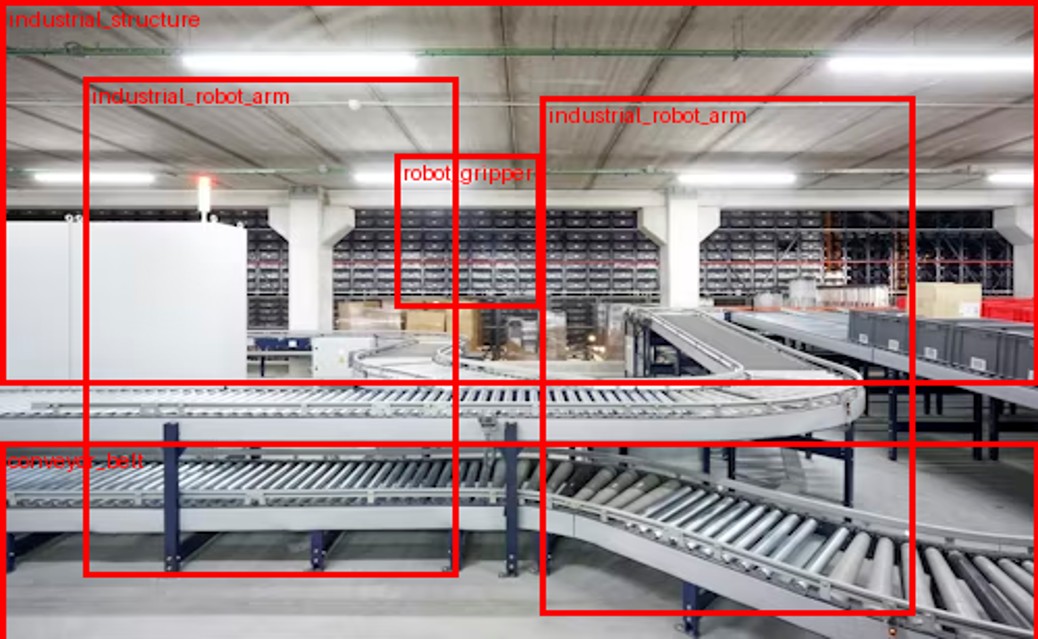
Industrial Annotation: Much More Than a Simple Technical Prerequisite
Industrial annotation is no longer limited to drawing boxes around objects. It now encompasses advanced tasks such as segmentation, fine-grained classification, and interpretation of complex scenes. This evolution is directly tied to the requirements of modern industrial applications, which demand robust and reliable deep learning models.
2D and 3D annotation enables the integration of essential spatial dimensions, particularly in environments where understanding depth, volume, and distance is critical. Without this level of precision, industrial computer vision cannot achieve the expected performance levels.
The Limits of Manual Annotation at Large Scale
With the explosion of data generated by industrial systems, manual annotation quickly reaches its limits. Modern production lines generate continuous streams of images and 3D data, making exhaustive annotation costly and difficult to scale.
In this context, annotation automation becomes a necessity. It accelerates development cycles while maintaining the consistency required to train high-performing deep learning models.
Automation of Annotation: Towards Human-Machine Hybrid Pipelines
Annotation automation relies on computer vision models capable of producing pre-annotations, which are then validated and adjusted by experts. This hybrid approach combines the speed of algorithms with the precision of human expertise.
Active learning techniques focus annotation efforts on the most relevant data. This strategy is particularly suited to industrial contexts, where certain defects are rare but critical. 2D and 3D annotation, combined with intelligent segmentation mechanisms, thus becomes more effective and targeted.
Multi-Modal Annotation and the Increasing Complexity of Industrial Data
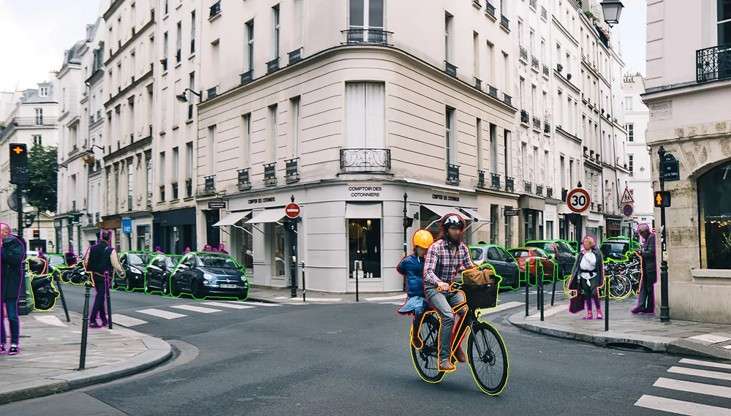
Modern industrial systems rely on a combination of heterogeneous data: 2D images, 3D point clouds, thermal data, and IoT sensors. Computer vision is evolving towards a multi-modal approach that requires coherent and synchronized annotation across these different sources.
Segmentation applied to 3D data, for example, allows a full understanding of an industrial environment, opening the door to advanced applications in robotics and automation
Generative AI for Industrial Annotation
Generative AI introduces new possibilities for industrial annotation, particularly through the creation of realistic synthetic data. These data allow simulation of rare situations, complex defects, or dangerous scenarios that are difficult to capture in real life.
However, using generated data requires rigorous validation. 2D and 3D annotation applied to synthetic data must meet the same quality standards as real-world data to ensure the reliability of trained deep learning models.
Towards a Data-Centric Approach to Industrial AI
Industry is progressively adopting a data-centric approach, in which continuous improvement of data takes precedence over increasing model complexity. In this perspective, fine segmentation, annotation consistency, and coverage of edge cases become major levers of performance.
2D and 3D annotation thus fits into an evolving process, fueled by field feedback and errors detected in production, reinforcing the robustness of computer vision systems
Evolving Roles and Governance of Annotated Data: The roles in industrial annotation are evolving toward greater expertise and responsibility. Annotators are becoming experts capable of interpreting complex environments and guiding deep learning models through high-quality annotations.
The governance of annotated data, supported by roles such as data stewards, ensures the consistency, traceability, and compliance of datasets over time—an essential requirement for industrial computer vision.
Safety, Compliance, and Industrial Responsibility
In industry, an annotation error can have major consequences. Computer vision often operates in critical contexts, where operator safety and production continuity are at stake.
2D and 3D annotation and segmentation must therefore be carried out within strict safety and compliance frameworks to ensure reliable and responsible systems
Conclusion – Annotation: The Invisible Foundation of Augmented Industry
The future of industrial data annotation relies on an intelligent combination of automation, generative AI, and human expertise. Computer vision will continue to advance, driven by deep learning breakthroughs, but its success will depend primarily on the quality of annotated data.
2D and 3D annotation and segmentation are emerging as strategic pillars of industrial AI. Companies that can structure these processes will gain a lasting competitive advantage in an increasingly data-driven industrial world.